Objectives
2. To determine the applicability of different turbulence models over the specified range of Reynolds numbers.

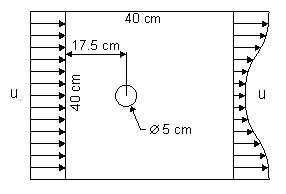
Calculations, Results, and Discussion
2. Run the simulations, using the two different turbulence models available in the CFX package (k-e and k-e RNG), until a steady state is reached.
3. Determine the velocity and pressure distributions before and after the cylinder using CFX-visualize.
4. By numerically integrating the distributions from step 3, find the drag on the cylinder and then the drag coefficient of the cylinder.
5. Do both turbulence models give the same results? How well do the results agree with known values?